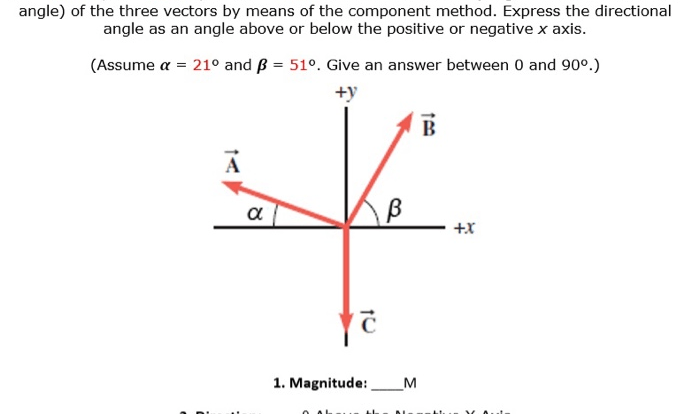
Intro to quantum mechanics griffiths solutions – Embark on an illuminating journey into the enigmatic realm of quantum mechanics with our comprehensive guide to Griffiths’ introductory text. Delving into the fundamental concepts of wave-particle duality, superposition, and entanglement, this resource unveils the captivating intricacies of the quantum world, empowering you with a profound understanding of its applications and implications.
Through a series of engaging chapters, we meticulously explore the Schrödinger equation, quantum operators, measurement, and the diverse applications of quantum mechanics, ranging from the behavior of atoms and molecules to the frontiers of computing and medicine. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of the quantum realm, transforming your understanding of the physical world.
1. Overview of Quantum Mechanics

Quantum mechanics is a branch of physics that deals with the behavior of matter and energy at the atomic and subatomic level. It is based on the idea that all matter has both wave-like and particle-like properties, and that these properties can only be explained by using mathematical equations.
One of the most important concepts in quantum mechanics is wave-particle duality. This concept states that all matter has both wave-like and particle-like properties. For example, light can behave like a wave when it is diffracted through a narrow slit, but it can also behave like a particle when it interacts with matter.
Another important concept in quantum mechanics is superposition. This concept states that a particle can be in multiple states at the same time. For example, an electron can be in a state where it is both spinning up and spinning down at the same time.
Quantum mechanics has a wide range of applications in the real world. For example, it is used to explain the behavior of lasers and transistors. It is also used to develop new technologies, such as quantum computers and quantum cryptography.
2. The Schrödinger Equation

The Schrödinger equation is a mathematical equation that describes the wave function of a particle. The wave function is a mathematical function that contains all of the information about the particle, including its position, momentum, and energy.
The Schrödinger equation can be used to calculate the wave function of a particle in any given situation. For example, it can be used to calculate the wave function of an electron in an atom or the wave function of a photon in a laser.
The Schrödinger equation has been used to solve many important problems in physics. For example, it has been used to explain the behavior of atoms, molecules, and solids. It has also been used to develop new technologies, such as lasers and transistors.
3. Quantum Operators
Quantum operators are mathematical operators that are used to represent physical quantities in quantum mechanics. For example, the position operator is used to represent the position of a particle, and the momentum operator is used to represent the momentum of a particle.
Quantum operators can be used to make predictions about the behavior of particles. For example, the position operator can be used to predict the probability of finding a particle at a given location, and the momentum operator can be used to predict the probability of finding a particle with a given momentum.
Quantum operators are essential for understanding the behavior of matter and energy at the atomic and subatomic level.
4. Measurement in Quantum Mechanics
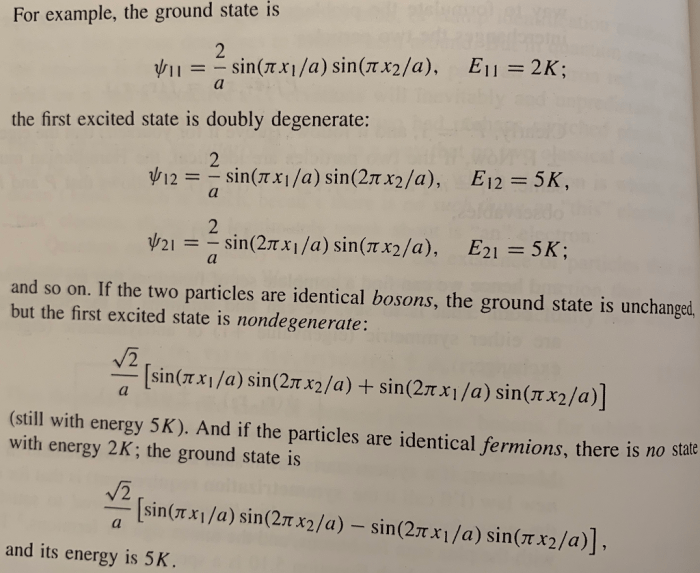
Measurement in quantum mechanics is the process of observing a physical quantity and obtaining a value for that quantity.
When a measurement is made, the wave function of the particle collapses, and the particle is said to be in a definite state. For example, if the position of an electron is measured, the wave function of the electron will collapse, and the electron will be in a definite position.
The collapse of the wave function is one of the most important and mysterious aspects of quantum mechanics. It is not yet fully understood why the wave function collapses when a measurement is made.
5. Applications of Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics has a wide range of applications in the real world. For example, it is used to explain the behavior of lasers and transistors. It is also used to develop new technologies, such as quantum computers and quantum cryptography.
Quantum mechanics is also used in a variety of other fields, such as chemistry, biology, and medicine. For example, it is used to explain the behavior of atoms and molecules, and it is used to develop new drugs and treatments for diseases.
Question Bank: Intro To Quantum Mechanics Griffiths Solutions
What is the significance of the Schrödinger equation in quantum mechanics?
The Schrödinger equation is a fundamental equation that governs the behavior of quantum systems. It provides a mathematical framework for calculating the wave function of a particle, which contains information about its state and dynamics.
How do quantum operators contribute to our understanding of quantum mechanics?
Quantum operators are mathematical tools that represent physical quantities, such as position, momentum, and energy. They allow us to make predictions about the behavior of particles and understand the interactions between different quantum systems.
What are some practical applications of quantum mechanics?
Quantum mechanics has numerous applications in various fields, including computing, cryptography, medicine, and materials science. It has led to the development of technologies such as lasers, transistors, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).