Delving into the intricacies of Mediterranean climate ap human geography, this comprehensive guide unveils the defining characteristics, influential factors, and diverse landscapes that shape this unique climatic region.
Mediterranean climates, renowned for their warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters, are found in various regions worldwide, including the Mediterranean Basin, parts of California, central Chile, and southwestern Australia. These regions experience distinct seasonal temperature and precipitation patterns, influenced by a combination of latitude, altitude, proximity to water bodies, and prevailing wind patterns.
Mediterranean Climate Overview
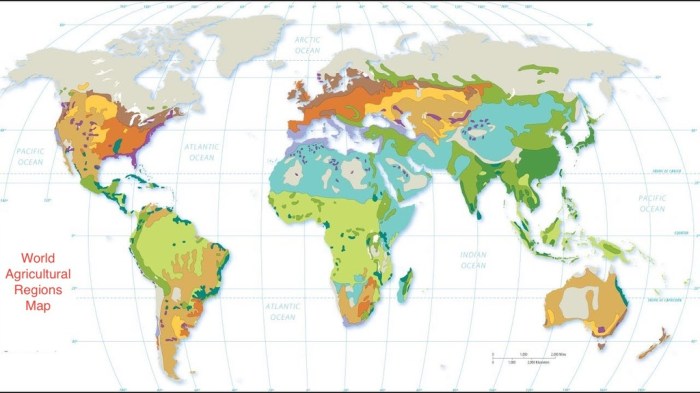
Mediterranean climates are characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. They are found in regions around the Mediterranean Sea, as well as in parts of California, Chile, South Africa, and Australia.
During the summer, Mediterranean climates experience high temperatures and little rainfall. The average temperature in July is typically between 20°C and 25°C. The skies are usually clear, and there is little wind.
In the winter, Mediterranean climates experience mild temperatures and more rainfall. The average temperature in January is typically between 5°C and 10°C. The skies are often cloudy, and there is more wind.
Seasonal Temperature and Precipitation Patterns
The seasonal temperature and precipitation patterns in Mediterranean climates are caused by the region’s location and topography.
The Mediterranean Sea acts as a heat reservoir, which helps to keep temperatures mild during the winter. The mountains that surround the Mediterranean Sea also help to protect the region from cold air masses.
The prevailing wind patterns in the Mediterranean region are from the west. These winds bring moisture from the Atlantic Ocean, which helps to produce rainfall during the winter.
Factors Influencing Mediterranean Climate
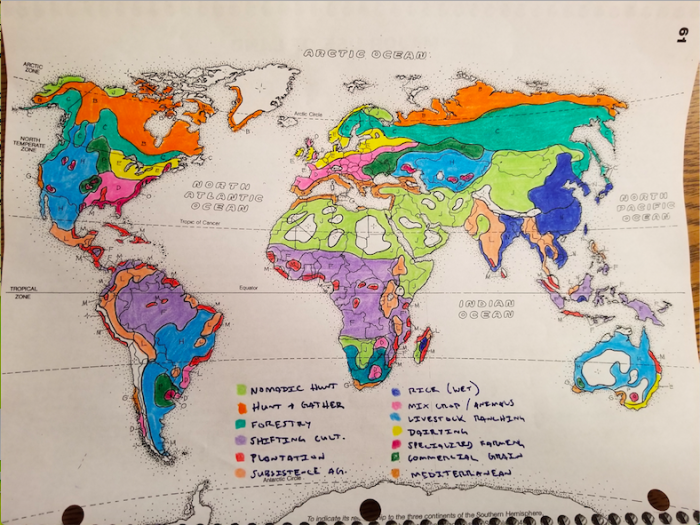
Latitude and Altitude
The latitude and altitude of a region can influence its Mediterranean climate.
Regions that are located at higher latitudes or altitudes tend to have cooler temperatures and more rainfall than regions that are located at lower latitudes or altitudes.
The Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean climate ap human geography
The Mediterranean Sea has a significant influence on the climate of the regions that surround it.
The Mediterranean Sea acts as a heat reservoir, which helps to keep temperatures mild during the winter. The Mediterranean Sea also provides moisture for rainfall during the winter.
Prevailing Wind Patterns
The prevailing wind patterns in the Mediterranean region are from the west.
These winds bring moisture from the Atlantic Ocean, which helps to produce rainfall during the winter.
Vegetation and Landforms in Mediterranean Climate Regions
Plant Communities
The plant communities found in Mediterranean climate regions are adapted to the region’s unique climate conditions.
- Evergreen trees: Evergreen trees are common in Mediterranean climate regions. These trees have leaves that remain green throughout the year. This helps them to survive the dry summers.
- Shrubs: Shrubs are also common in Mediterranean climate regions. Shrubs are typically shorter than trees, and they have smaller leaves. This helps them to conserve water during the dry summers.
- Herbs: Herbs are another common type of plant found in Mediterranean climate regions. Herbs are typically low-growing plants with soft stems.
Landforms
The landforms found in Mediterranean climate regions are also influenced by the region’s unique climate conditions.
The most common landforms in Mediterranean climate regions are:
- Mountains: Mountains are common in Mediterranean climate regions. Mountains help to protect the region from cold air masses.
- Hills: Hills are also common in Mediterranean climate regions. Hills are typically smaller than mountains.
- Plateaus: Plateaus are another common landform in Mediterranean climate regions. Plateaus are large, flat areas of land.
Human Activities in Mediterranean Climate Regions
Agriculture
Agriculture is a major economic activity in Mediterranean climate regions.
The most common crops grown in Mediterranean climate regions are:
- Grapes: Grapes are a major crop in Mediterranean climate regions. Grapes are used to make wine, raisins, and other products.
- Olives: Olives are another major crop in Mediterranean climate regions. Olives are used to make olive oil, soap, and other products.
- Wheat: Wheat is also a major crop in Mediterranean climate regions. Wheat is used to make bread, pasta, and other products.
Tourism
Tourism is another major economic activity in Mediterranean climate regions.
The Mediterranean climate regions are popular tourist destinations because of their beautiful scenery, mild climate, and rich history.
Cultural and Historical Significance
The Mediterranean climate regions have a rich cultural and historical significance.
The Mediterranean climate regions were home to some of the world’s earliest civilizations, including the ancient Greeks and Romans.
FAQ Resource: Mediterranean Climate Ap Human Geography
What are the defining characteristics of a Mediterranean climate?
Mediterranean climates are characterized by warm, dry summers with little to no precipitation and mild, wet winters with moderate rainfall.
What factors influence the formation of Mediterranean climates?
Latitude, altitude, proximity to water bodies, and prevailing wind patterns all play a role in shaping Mediterranean climate patterns.
What types of vegetation are commonly found in Mediterranean climate regions?
Mediterranean climate regions are home to a diverse array of plant communities, including evergreen forests, shrublands, and grasslands.
